Advancing Infusion Therapy Through Primary and Secondary Tubing Systems
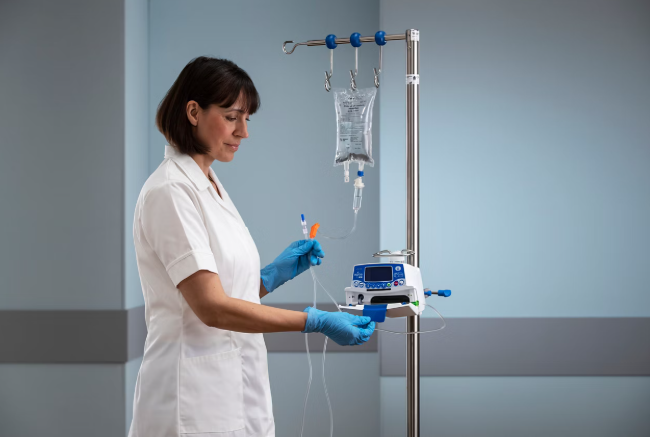

The Primary & Secondary IV Tubing industry plays a crucial role in modern healthcare by enabling the safe and efficient delivery of fluids, medications, and nutrients to patients. While these systems may appear simple at first glance, their design, quality, and functionality directly impact patient safety, treatment accuracy, and clinical efficiency. Among the essential components in infusion therapy, primary tubing is the backbone of fluid delivery, connecting the main fluid source to the patient and ensuring uninterrupted flow.
This article explores the significance of primary tubing, differentiates between primary and secondary IV tubing, and highlights their applications and benefits in various healthcare settings.
Understanding Primary and Secondary IV Tubing
IV tubing systems are designed to administer fluids directly into a patient’s bloodstream, often through a central or peripheral line. The system typically consists of tubing, connectors, drip chambers, and flow regulators. In multi-drug or complex fluid therapy scenarios, the distinction between primary and secondary tubing becomes critical.
Primary tubing refers to the main line that connects the fluid container—such as an IV bag or bottle—to the patient. It is responsible primary tubing for delivering the bulk of fluids, whether for hydration, nutrition, or medication. Secondary tubing, often called a piggyback line, is connected to the primary line and allows for additional medications or fluids to be administered intermittently without disrupting the primary infusion. This dual-line system enables clinicians to manage multiple therapies simultaneously while maintaining accuracy and patient safety.
The Role of Primary Tubing in Infusion Therapy
Primary tubing is fundamental to infusion therapy because it carries the main flow of fluids from the source to the patient. High-quality primary tubing must be flexible, durable, and free of kinks or leaks to ensure consistent delivery. Its transparency allows healthcare providers to monitor fluid flow, detect air bubbles, and quickly identify any irregularities in the system.
In many clinical settings, primary tubing is used in combination with flow regulators and drip chambers to maintain a precise rate of infusion. For therapies requiring long-term or continuous administration, such as parenteral nutrition or critical care medications, reliable primary tubing is essential to avoid interruptions and ensure patient safety.
Applications of Primary and Secondary IV Tubing
Primary Tubing Applications
Primary tubing is versatile and widely used across various healthcare scenarios. Common applications include:
- Hydration Therapy: Delivering fluids to patients suffering from dehydration, illness, or post-surgery recovery.
- Medication Delivery: Administering critical medications such as antibiotics, electrolytes, and pain management solutions.
- Parenteral Nutrition: Providing essential nutrients to patients who cannot consume food orally, requiring continuous and precise infusion.
- Blood Products: Transporting blood or plasma safely to patients in need, ensuring that flow is consistent and controlled.
Secondary Tubing Applications
Secondary tubing allows for additional medications or fluids to be delivered without interrupting the primary infusion. Common uses include:
- Medication Piggybacking: Administering intermittent doses of medications like antibiotics or chemotherapeutic agents.
- Supplemental Fluids: Adding electrolytes or vitamins to ongoing hydration therapy.
- Short-Duration Infusions: Delivering medications that require precise timing and short infusion periods without affecting the main therapy.
Components of Primary and Secondary IV Tubing
Tubing Material
The tubing must be made from high-quality, medical-grade materials that are flexible, durable, and compatible with a variety of fluids. Primary tubing is usually longer and thicker to handle the main infusion, while secondary tubing is shorter and designed for intermittent use. Both types must resist kinking, leakage, and chemical degradation.
Drip Chambers
Drip chambers are an integral part of both primary and secondary tubing systems. They allow healthcare providers to monitor flow rates, eliminate air bubbles, and regulate infusion speed. In primary tubing, drip chambers are typically larger to accommodate higher fluid volumes, while secondary tubing drip chambers are smaller for controlled, intermittent delivery.
Connectors and Safety Features
Connectors attach the tubing to the fluid container and the patient’s catheter. Modern IV sets often feature needle-free connectors, anti-reflux valves, and air-elimination filters. These safety mechanisms reduce the risk of infection, contamination, and accidental injury, which is especially important in long-term or multi-drug therapies.
Flow Regulators
Flow regulators, whether manual or electronic, control the speed of infusion in both primary and secondary tubing. Accurate regulation is particularly critical in pediatric care, critical care, and treatments that require precise dosing. Electronic infusion pumps integrated with primary tubing enhance accuracy and reduce human error.
Advantages of Primary Tubing
Primary tubing offers several essential benefits in healthcare delivery:
- Continuous Flow: Ensures that patients receive a steady supply of fluids or medications.
- Versatility: Compatible with a wide range of fluids, medications, and infusion setups.
- Accuracy: Supports precise dosing and timing, particularly when used with flow regulators and electronic pumps.
- Integration with Secondary Tubing: Allows additional medications or fluids to be administered without disrupting the primary infusion.
Safety Considerations and Infection Control
Even with advanced IV systems, proper handling, monitoring, and maintenance are essential to prevent complications.
- Sterility: All components, including primary tubing, must remain sterile before and during use.
- Air Management: Drip chambers and tubing design help prevent air bubbles from entering the bloodstream.
- Routine Monitoring: Healthcare providers should regularly check flow rates, connections, and tubing integrity to ensure safe and effective infusion therapy.
Applications Across Healthcare Settings
Hospitals and Critical Care Units
Hospitals rely heavily on primary and secondary tubing systems. Intensive care units, operating theaters, and oncology wards require accurate, continuous infusion, and primary tubing provides the backbone for these therapies. Secondary tubing allows for medication piggybacking without interrupting the main infusion.
Homecare and Long-Term Treatment
Home healthcare increasingly depends on reliable IV systems. Patients recovering from surgery or managing chronic illnesses can benefit from primary tubing for continuous hydration or medication delivery, with secondary tubing providing flexibility for intermittent therapies.
Outpatient Clinics and Specialty Centers
Outpatient facilities use primary and secondary tubing for hydration, medication administration, and short-term infusions. High-quality tubing and connectors ensure efficiency, patient comfort, and safety in these environments.
See also: The Importance of Therapy in Addiction Recovery and Mental Health Healing
Innovations in IV Tubing
Smart Infusion Systems
Electronic infusion pumps integrated with primary tubing allow automated flow control, real-time monitoring, and alerts for occlusions or irregular flow. These smart systems reduce human error and enhance patient safety.
Advanced Materials
Latex-free, chemically resistant, and flexible tubing improves durability and minimizes the risk of allergic reactions. Antimicrobial coatings further reduce infection risk during infusion therapy.
Sustainable Solutions
Environmental concerns have prompted the development of recyclable and biodegradable tubing systems without compromising safety or performance.
Future Outlook
The demand for primary and secondary IV tubing is expected to grow due to increasing healthcare infrastructure, rising chronic illnesses, and expanding homecare services. Future innovations are likely to focus on:
- Smart, Connected Devices: Real-time monitoring integrated with electronic health records.
- Enhanced Safety Features: Improved anti-reflux valves, air filtration, and sterile packaging.
- Eco-Friendly Designs: Sustainable materials to reduce medical waste while maintaining performance and safety.
Conclusion
The Primary & Secondary IV Tubing industry is essential in modern healthcare, supporting accurate, safe, and efficient infusion therapy. Primary tubing forms the backbone of fluid delivery, ensuring continuous flow, precise dosing, and reliable performance. Secondary tubing adds flexibility for intermittent medication delivery without disrupting the main infusion.
By understanding the applications, advantages, and safety considerations of primary and secondary IV tubing, healthcare providers can improve patient outcomes, optimize clinical workflows, and maintain high standards of care across hospitals, outpatient clinics, and homecare environments. As the industry evolves, these tubing systems will continue to be critical tools in delivering high-quality healthcare.